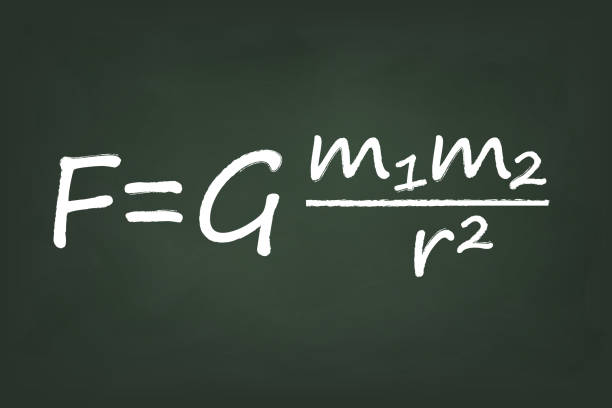What is Gravitation?
Gravitation is the fundamental force of attraction between objects with mass. According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. In simpler terms, gravity pulls objects towards each other. This force keeps planets in orbit around stars, moons around planets, and objects anchored to the Earth’s surface. Einstein’s theory of general relativity expanded our understanding of gravity by describing it as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy. Gravitation plays a crucial role in shaping the structure of the universe, influencing the motion of celestial bodies, and governing the dynamics of galaxies and the cosmos at large.

Gravitation is crucial for maintaining the structure of the universe, controlling celestial motions, and enabling the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets. It governs the orbits of planets around stars, moons around planets, and satellites around Earth. Without gravitation, celestial bodies would not stay in stable orbits, disrupting the fabric of the cosmos. Additionally, gravitation influences phenomena like tides on Earth, impacting ecosystems and coastal areas. Understanding gravity is essential for space exploration, satellite communication, and predicting astronomical events. It also plays a vital role in everyday life, keeping our feet firmly planted on the ground and objects from floating away.

Unlocking the Mysteries of Gravitation:
A Journey Through the Force That Shapes Our Universe:
Gravitation, the fundamental force that governs the motion of celestial bodies and shapes the structure of the universe, has captivated the minds of scientists and philosophers for centuries. From the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle to the groundbreaking theories of Sir Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein, humanity’s understanding of gravitation has evolved dramatically over time, leading to profound insights into the nature of space, time, and the cosmos.

Historical Perspectives:
From Aristotle to Newton:
The study of gravitation can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early thinkers grappled with questions about the motions of the stars, planets, and moons. Aristotle proposed a geocentric model of the universe, in which celestial bodies moved in perfect circles around the Earth. However, it was the revolutionary work of Isaac Newton in the 17th century that laid the foundation for our modern understanding of gravitation.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation, formulated in his masterpiece “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), stated that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This elegant mathematical expression provided a framework for explaining the motions of celestial bodies with remarkable precision, from the orbits of planets to the trajectories of comets.

Einstein’s Revolution:
The Curvature of Spacetime:
While Newton’s theory of gravitation was incredibly successful in describing the motions of objects in the solar system, it had limitations when applied to extreme conditions, such as near the speed of light or in the presence of very strong gravitational fields. These limitations prompted Albert Einstein to develop his general theory of relativity, which revolutionized our understanding of gravitation.

In Einstein’s theory, gravitation is not described as a force acting at a distance, but rather as the curvature of spacetime caused by the presence of mass and energy. According to general relativity, massive objects like planets and stars warp the fabric of spacetime around them, creating gravitational fields that influence the motion of other objects. The famous analogy often used to illustrate this concept is that of a heavy ball placed on a stretched rubber sheet, causing nearby objects to roll towards it.
Black Holes and Cosmic Phenomena:
General relativity has led to the prediction and discovery of numerous exotic phenomena, including black holes, gravitational waves, and the bending of light around massive objects. Black holes, for example, are regions of spacetime where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from them. These enigmatic objects have captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike, serving as laboratories for testing the boundaries of our current understanding of physics.
Gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of spacetime caused by the acceleration of massive objects, were predicted by Einstein’s theory and finally detected in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO). This groundbreaking discovery opened up a new window into the universe, allowing scientists to observe phenomena that were previously invisible to traditional telescopes.
Challenges and Frontiers:
Despite the tremendous progress made in understanding gravitation, there are still many unanswered questions and challenges that remain. One of the most pressing issues in modern physics is the quest to reconcile general relativity with quantum mechanics, the theory that describes the behavior of particles on the smallest scales. These two pillars of physics are highly successful in their respective domains, but they are fundamentally incompatible with each other in certain regimes, such as at the center of black holes or during the earliest moments of the universe.
Efforts to develop a unified theory of quantum gravity, which would seamlessly merge general relativity and quantum mechanics into a single framework, have been ongoing for decades. String theory, loop quantum gravity, and other approaches represent promising avenues of research in this endeavor, offering new insights into the nature of spacetime and the fundamental structure of reality.
Conclusion:
Exploring the Depths of Gravitation:
Gravitation stands as one of the most profound and mysterious forces in the universe, shaping the cosmos on the grandest scales and influencing the behavior of matter and energy throughout space and time. From the ancient speculations of Aristotle to the revolutionary insights of Newton and Einstein, humanity’s quest to understand gravitation has led to paradigm shifts in our understanding of the nature of reality.
As we continue to explore the depths of gravitation through theoretical speculation, experimental observation, and technological innovation, we are certain to uncover new mysteries and unlock new realms of knowledge that will deepen our appreciation of the intricate tapestry of the cosmos.
The journey to comprehend the force of gravitation has been long and arduous, yet each step along the way has illuminated new facets of the universe and expanded our understanding of the laws that govern its behavior. As we peer ever deeper into the mysteries of gravitation, we are reminded of the boundless curiosity and ingenuity of the human spirit, driving us forward on a quest to unravel the secrets of the cosmos.