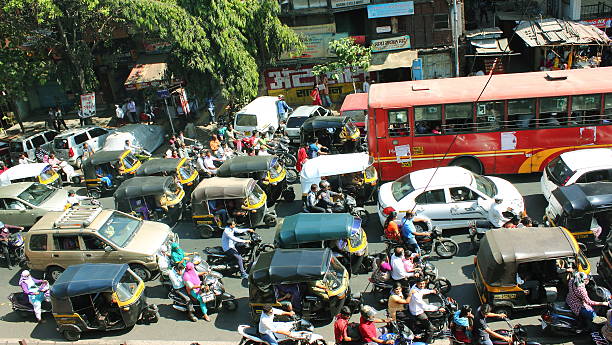Outline on Noise Pollution
Noise pollution refers to the excessive or disruptive sound that disturbs the peace, harms health, or degrades the environment. Unlike other forms of pollution, noise dissipates quickly once the source is removed, but its effects can be lasting and profound. Common sources of noise pollution include transportation, industrial activities, and urbanization.
1. Introduction to Noise Pollution
– Definition and significance
– Types of sources
2. Sources of Noise Pollution
– Transportation (e.g., roads, airports, railways)
– Industrial and construction activities
– Urbanization and high-density living
– Entertainment and social events (e.g., concerts, fireworks, sports)
3. Health and Environmental Effects
– Human health impacts (e.g., hearing loss, stress, cardiovascular issues, sleep disturbances)
– Environmental impacts (e.g., disruption of wildlife, ecosystem imbalance)
4. Social and Economic Consequences
– Quality of life effects (e.g., reduced comfort, stress, decreased property values)
– Impact on productivity and work environments
5. Legislation and Regulations
– Overview of national and local noise control laws
– Standards and guidelines from organizations like WHO
6. Mitigation Strategies
– Urban planning and zoning for noise reduction
– Technological solutions (e.g., sound barriers, soundproofing, quiet vehicles)
– Noise control at source (e.g., regulations on industries, transportation)
– Public awareness and education on noise reduction
7. Community and Personal Actions
– Individual steps to reduce noise exposure
– Community initiatives for quieter environments
– Advocacy for noise control policies
8. Conclusion
– Summary of the importance of noise pollution control
– The need for collective action and continued efforts to reduce noise pollution.
Noise Pollution: Understanding Its Sources, Impact, and Solutions
Introduction to Noise Pollution
In our bustling world, filled with the sounds of traffic, construction, and modern technology, noise has become a constant companion. While some noise is a normal part of urban life, excessive or unwanted noise can cross into the territory of noise pollution. This type of pollution is not just an irritant—it can have serious effects on our health, well-being, and the environment. This article explores the sources of noise pollution, its impact on humans and nature, and what we can do to mitigate it.
What is Noise Pollution?
Noise pollution refers to the excessive or disruptive sound that disturbs the peace, harms health, or degrades the environment. Unlike other forms of pollution, noise dissipates quickly once the source is removed, but its effects can be lasting and profound. Common sources of noise pollution include transportation, industrial activities, and urbanization.
Major Sources of Noise Pollution
Transportation
Transportation systems are among the largest contributors to noise pollution. The constant hum of traffic, the roar of airplanes, and the rumble of trains create a cacophony of sounds. Urban areas with dense traffic and proximity to airports are particularly prone to high levels of transportation-related noise.
Industrial and Construction Activities
Industrial and construction activities generate significant noise. Heavy machinery, equipment, and the general bustle of industrial zones can create a steady stream of loud sounds. Construction projects, especially in urban areas, can also contribute to heightened noise levels.
Urbanization
As cities grow and become more populated, noise levels tend to increase. Dense housing, commercial areas, and entertainment venues add to the urban soundscape, making it difficult to escape from the constant noise.
Entertainment and Social Events
Loud music at concerts, the crackling of fireworks, and the cheers at sports events are all sources of noise pollution. These events can disrupt communities, especially when they occur near residential areas.
Health and Environmental Effects of Noise Pollution
The effects of noise pollution go beyond simple annoyance. It can have significant impacts on human health and the environment.
Human Health Impacts
Short-term effects: Exposure to loud noise can lead to stress, irritability, and sleep disturbances. This can affect productivity and overall quality of life.
Long-term effects: Continuous exposure to noise pollution can cause hearing loss, increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and impair cognitive function. Studies suggest that constant noise can elevate stress hormones, leading to long-term health complications.
Environmental Impacts
Noise pollution doesn’t just affect humans; it can have far-reaching effects on the environment:
Wildlife disruption: Loud noises can interfere with animal communication, breeding, and migration patterns. Birds and marine life, in particular, are sensitive to noise pollution.
Ecosystem imbalance: Noise can alter predator-prey dynamics, leading to changes in animal behavior and potentially impacting entire ecosystems.
Social and Economic Consequences
Noise pollution also carries social and economic consequences. It can reduce the quality of life for those living in noisy areas and decrease property values. In workplaces, excessive noise can decrease productivity, leading to economic losses for businesses.
Addressing Noise Pollution: Legislation and Regulations
To combat noise pollution, governments and organizations have established various laws and guidelines. These aim to control noise levels and protect public health.
National and Local Laws
Many countries have enacted noise control laws to regulate the permissible noise levels in different areas. These laws often specify acceptable decibel levels for residential, commercial, and industrial zones, and outline the hours during which loud activities are prohibited.
Standards and Guidelines
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) have published guidelines on acceptable noise levels to help governments and communities understand and manage noise pollution. These standards provide benchmarks for legislation and help inform public policy.
Strategies for Reducing Noise Pollution
There are several effective strategies to reduce noise pollution, both at the community level and on a personal level.
Urban Planning and Zoning
Effective urban planning can play a crucial role in reducing noise pollution. By zoning industrial and commercial areas away from residential neighborhoods, communities can minimize noise exposure. Green spaces and noise barriers can also help absorb or deflect noise.
Technological Solutions
Technological advances offer new ways to mitigate noise. Sound barriers along highways, quieter vehicles, and soundproofing materials in buildings are all examples of technology’s role in reducing noise pollution. These solutions can be costly, but they offer significant benefits.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about the dangers of noise pollution is key to combating it. Public campaigns, school programs, and community events can educate people about noise pollution’s impact and encourage them to take steps to reduce their noise footprint.
Noise Control at the Source
One of the most effective ways to reduce noise pollution is to control it at the source. This involves implementing regulations on industries, transportation, and other sources of noise. For example, governments can mandate quieter engines in vehicles and require construction sites to operate within certain hours to minimize disruption.
Community and Personal Actions
While laws and regulations are important, individuals and communities can also take steps to reduce noise pollution.
Individual Steps
– Use ear protection in noisy environments to prevent hearing damage.
– Keep household noise levels down by choosing quieter appliances and using soft materials to absorb sound.
– Limit loud activities, such as playing loud music, to appropriate times of the day.
Community Initiatives
Communities can work together to create quieter environments. This might include advocating for noise barriers, promoting green spaces, or establishing noise-reduction ordinances. Engaging with local government to address noise issues can lead to meaningful change.
Advocacy and Involvement
Joining or forming advocacy groups that focus on noise pollution can help bring attention to the issue and push for policy changes. Participating in local government meetings and engaging with elected officials can also be effective ways to advocate for noise control policies.
Conclusion
Noise pollution is a significant issue that affects both human health and the environment. Its sources are varied, from transportation to industrial activities, and its impacts can be severe. However, with proper awareness, legislation, and community action, noise pollution can be mitigated. Addressing this problem requires a collective effort at the local, national, and global levels to create a quieter and healthier world.